0- 前置条件
安装jdk和tomcat
我这里选择同一台服务器安装两个tomcat,一个tomcat作为Jenkins的容器,另外一个tomcat作为简单mvc项目的部署服务器。
Jenkins服务器使用8080端口,mvc项目tomcat使用8081端口。
1 - 部署Jenkins
官网下载http://jenkins-ci.org/
我下载的是最新的2.5版本
下载得到一个jenkins.war的war包
可以直接使用java -j jenkins.war运行,或者把war包放到tomcat运行
我这里是放到tomcat,启动tomcat即可.
启动后可以在http://localhost:8080/jenkins/,看到Jenkins已经在运行
第一次进入,需要你输入一个key,会提示您在/root/.jenkins/…某个路径下找到
进入后会提示你安装一些插件,根据需要安装即可,或者直接安装它提供的一键建议安装.
2 - 安装相关插件
我这里需要git plugin和maven plugin,可以在插件管理处搜索安装。
这两个基本是默认安装好了的.
3 - 安装git和maven
安装git1
yum install git
安装maven1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
291、官网找到最新版的安装包:
http://maven.apache.org/download.cgi
拷贝文件名为 *-bin.tar.gz 的链接地址;
2、下载
# wget http://mirrors.hust.edu.cn/apache/maven/maven-3/3.3.3/binaries/apache-maven-3.3.3-bin.tar.gz
3、解压
# tar xvf apache-maven-3.3.3-bin.tar.gz
如果需要:移动到其他目录
建立软连接:# ln -s apache-maven-3.3.3 maven
4、配置环境变量
# vi /etc/profile
export M2_HOME=/usr/local/apache-maven
export PATH=$PATH:$M2_HOME/bin
# source /etc/profile
5、验证是否安装成功
# mvn -version
Apache Maven 3.3.3 (7994120775791599e205a5524ec3e0dfe41d4a06; 2015-04-22T19:57:37+08:00)
Maven home: /opt/app/maven
Java version: 1.8.0_51, vendor: Oracle Corporation
Java home: /usr/java/jdk1.8.0_51/jre
Default locale: zh_CN, platform encoding: UTF-8
OS name: "linux", version: "3.10.0-229.el7.x86_64", arch: "amd64", family: "unix"
4 - 配置jdk和maven路径等
选择”系统管理” -> “Global Tool Configuration”
在里面配置好jdk,maven的路径,只需要配置它们的根路径.
5 - 创建任务,配置项目信息
选择“新建”,填写项目任务名,并选择“构建一个maven项目”,保存.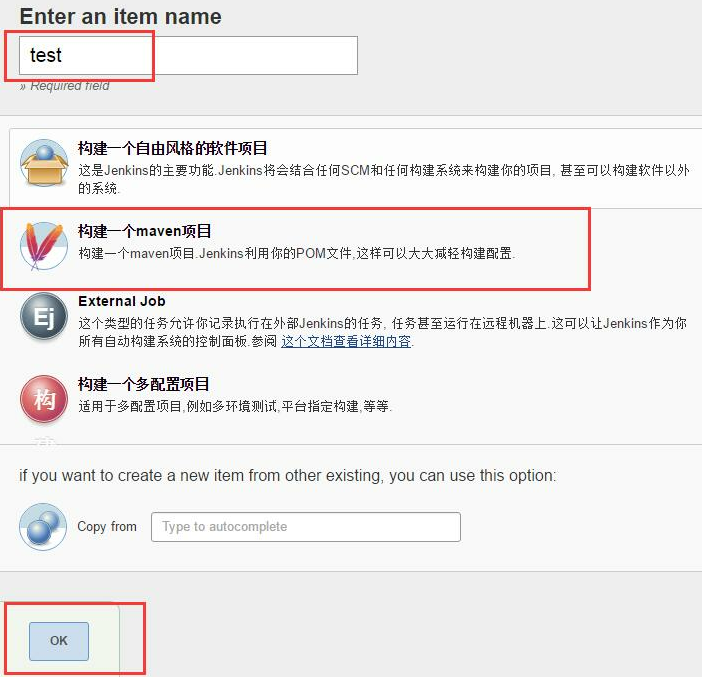
进入项目配置.
填写项目名称
填写Repository URL
我这里使用的是一个git上的一个建议springmvc项目
https://github.com/bingyue/easy-springmvc-maven
如果需要,也可以配置一下构建后发送邮件到您的邮箱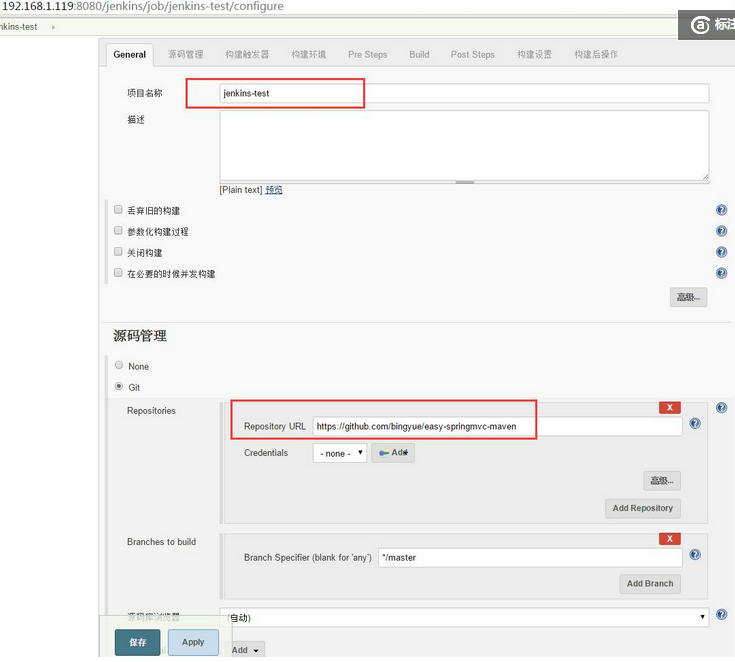
6 - 配置构建成功后的动作,添加shell
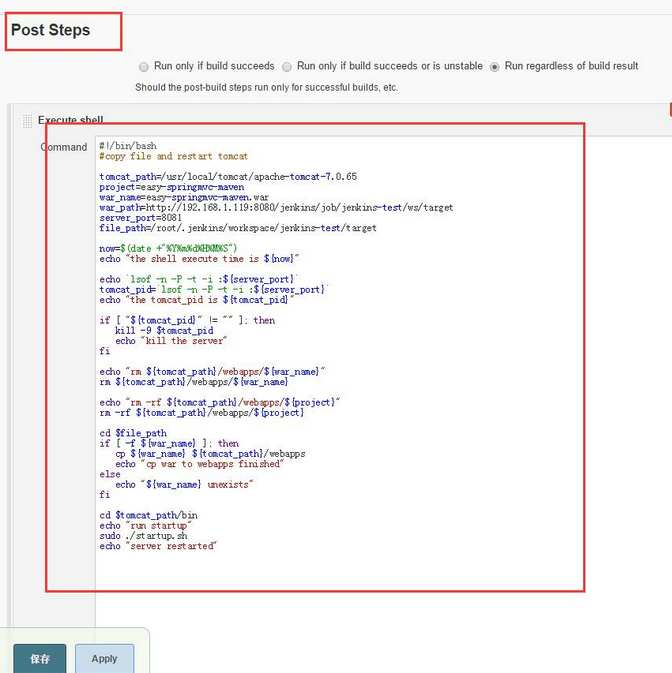
配置项目中的“Post Steps”,设置构建完成后的动作.
这里我设置为将war包拷贝到Tomcat目录,删除项目原来的内容文件夹,并重启Tomcat。
选择Run only if build succeeds or is unstable ,点击添加Execute Shell:
shell脚本:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40#!/bin/bash
#copy file and restart tomcat
tomcat_path=/usr/local/tomcat/apache-tomcat-7.0.65
project=easy-springmvc-maven
war_name=easy-springmvc-maven.war
war_path=http://192.168.1.119:8080/jenkins/job/jenkins-test/ws/target
server_port=8081
file_path=/root/.jenkins/workspace/jenkins-test/target
now=$(date +"%Y%m%d%H%M%S")
echo "the shell execute time is ${now}"
echo `lsof -n -P -t -i :${server_port}`
tomcat_pid=`lsof -n -P -t -i :${server_port}`
echo "the tomcat_pid is ${tomcat_pid}"
if [ "${tomcat_pid}" != "" ]; then
kill -9 $tomcat_pid
echo "kill the server"
fi
echo "rm ${tomcat_path}/webapps/${war_name}"
rm ${tomcat_path}/webapps/${war_name}
echo "rm -rf ${tomcat_path}/webapps/${project}"
rm -rf ${tomcat_path}/webapps/${project}
cd $file_path
if [ -f ${war_name} ]; then
cp ${war_name} ${tomcat_path}/webapps
echo "cp war to webapps finished"
else
echo "${war_name} unexists"
fi
cd $tomcat_path/bin
echo "run startup"
sudo ./startup.sh
echo "server restarted"
我这里是在/usr/local/tomcat/apache-tomcat-7.0.65
这个路径下配置了另外一个tomcat来运行测试的web项目.
shell脚本启动tomcat的命令”./startup.sh”,注意要使用sudo
7 - 运行构建项目
打开项目的主面板,直接点击绿色的运行任务构建按钮。
done!
8 - 其他
这个例子使用了同一台服务器部署Jenkins和实际项目。
实际应用则常用法是Jenkins单独部署,
所有别的要部署的项目,自己拥有服务器,为每个项目都创建Jenkins任务,在项目编译成功后,到Jenkins服务器下载编译好的部署包,然后依旧使用shell脚本完成这一切。
并且,可以为不同的部署环境配置不同的任务。一切都是可以定制的。