前言
目前的应用系统,不管是企业级应用还是互联网应用,最终数据的一致性是每个应用系统都要面临的问题,随着分布式的逐渐普及,数据一致性更加艰难,但是也很难有银弹的解决方案,也并不是引入特定的中间件或者特定的开源框架能够解决的,更多的还是看业务场景,根据场景来给出解决方案。根据笔者最近几年的了解,总结了几个点,更多的应用系统在编码的时候,更加关注数据的一致性,这样系统才是健壮的。
基础理论相关
说起事务,目前的几个理论,ACID事务特性,CAP分布式理论,以及BASE等,ACID在数据库事务中体现,CAP和BASE则是分布式事务的理论,结合业务系统,例如订单管理,例如仓储管理等,可以借鉴这些理论,从而解决问题。
- ACID 特性
A(原子性)事务的原子操作单元,对数据的修改,要么全部执行,要么全部不执行;
C(一致性)在事务开始和完成时,数据必须保持一致状态,相关的数据规则必须应用于事务的修改,以保证数据的完整性,事务结束时,所有的内部数据结构必须正确;
I(隔离性)保证事务不受外部并发操作的独立环境执行;
D(持久性)事务完成之后,对于数据的修改是永久的,即使系统出现故障也能够保持; - CAP
C(一致性)一致性是指数据的原子性,在经典的数据库中通过事务来保障,事务完成时,无论成功或回滚,数据都会处于一致的状态,在分布式环境下,一致性是指多个节点数据是否一致;
A(可用性)服务一直保持可用的状态,当用户发出一个请求,服务能在一定的时间内返回结果;
P(分区容忍性)在分布式应用中,可能因为一些分布式的原因导致系统无法运转,好的分区容忍性,使应用虽然是一个分布式系统,但是好像一个可以正常运转的整体 - BASE
BA: Basic Availability 基本业务可用性;
S: Soft state 柔性状态;
E: Eventual consistency 最终一致性;
最终一致性的几种做法
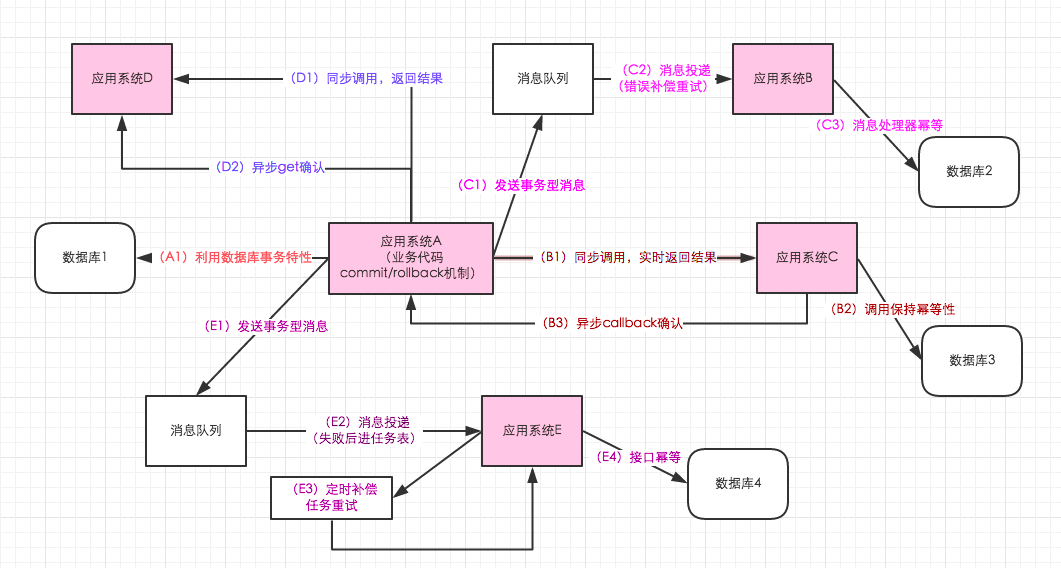
单数据库情况下的事务
如果应用系统是单一的数据库,那么这个很好保证,利用数据库的事务特性来满足事务的一致性,这时候的一致性是强一致性的。对于java应用系统来讲,很少直接通过事务的start和commit以及rollback来硬编码,大多通过spring的事务模板或者声明式事务来保证。
基于事务型消息队列的最终一致性
借助消息队列,在处理业务逻辑的地方,发送消息,业务逻辑处理成功后,提交消息,确保消息是发送成功的,之后消息队列投递来进行处理,如果成功,则结束,如果没有成功,则重试,直到成功,不过仅仅适用业务逻辑中,第一阶段成功,第二阶段必须成功的场景。对应上图中的C流程。
基于消息队列+定时补偿机制的最终一致性
前面部分和上面基于事务型消息的队列,不同的是,第二阶段重试的地方,不再是消息中间件自身的重试逻辑了,而是单独的补偿任务机制。其实在大多数的逻辑中,第二阶段失败的概率比较小,所以单独独立补偿任务表出来,可以更加清晰,能够比较明确的直到当前多少任务是失败的。对应上图的E流程。
业务系统业务逻辑的commit/rollback机制
这一点说的话确实不难,commit和rollback是数据库事务中的比较典型的概念,但是在系统分布式情况下,需要业务代码中实现这种,成功了commit,失败了rollback。
业务应用系统的幂等性控制
为啥要做幂等呢? 原因很简单,在系统调用没有达到期望的结果后,会重试。那重试就会面临问题,重试之后不能给业务逻辑带来影响,例如创建订单,第一次调用超时了,但是调用的系统不知道超时了是成功了还是失败了,然后他就重试,但是实际上第一次调用订单创建是成功了的,这时候重试了,显然不能再创建订单了。
查询
查询的API,可以说是天然的幂等性,因为你查询一次和查询两次,对于系统来讲,没有任何数据的变更,所以,查询一次和查询多次一样的。MVCC方案
多版本并发控制,update with condition,更新带条件,这也是在系统设计的时候,合理的选择乐观锁,通过version或者其他条件,来做乐观锁,这样保证更新及时在并发的情况下,也不会有太大的问题。例如update tablexxx set name=#name#,version=version+1 where version=#version# ,或者是 update tablexxx set quality=quality-#subQuality# where quality-#subQuality# >= 0 。单独的去重表
如果涉及到的去重的地方特别多,例如ERP系统中有各种各样的业务单据,每一种业务单据都需要去重,这时候,可以单独搞一张去重表,在插入数据的时候,插入去重表,利用数据库的唯一索引特性,保证唯一的逻辑。分布式锁
还是拿插入数据的例子,如果是分布是系统,构建唯一索引比较困难,例如唯一性的字段没法确定,这时候可以引入分布式锁,通过第三方的系统,在业务系统插入数据或者更新数据,获取分布式锁,然后做操作,之后释放锁,这样其实是把多线程并发的锁的思路,引入多多个系统,也就是分布式系统中得解决思路。删除数据
删除数据,仅仅第一次删除是真正的操作数据,第二次甚至第三次删除,直接返回成功,这样保证了幂等。插入数据的唯一索引
插入数据的唯一性,可以通过业务主键来进行约束,例如一个特定的业务场景,三个字段肯定确定唯一性,那么,可以在数据库表添加唯一索引来进行标示。API层面的幂等
这里有一个场景,API层面的幂等,例如提交数据,如何控制重复提交,这里可以在提交数据的form表单或者客户端软件,增加一个唯一标示,然后服务端,根据这个UUID来进行去重,这样就能比较好的做到API层面的唯一标示。状态机幂等
在设计单据相关的业务,或者是任务相关的业务,肯定会涉及到状态机,就是业务单据上面有个状态,状态在不同的情况下会发生变更,一般情况下存在有限状态机,这时候,如果状态机已经处于下一个状态,这时候来了一个上一个状态的变更,理论上是不能够变更的,这样的话,保证了有限状态机的幂等。
异步回调机制的引入
A应用调用B,在同步调用的返回结果中,B返回成功给到A,一般情况下,这时候就结束了,其实在99.99%的情况是没问题的,但是有时候为了确保100%,记住最起码在系统设计中100%,这时候B系统再回调A一下,告诉A,你调用我的逻辑,确实成功了。其实这个逻辑,非常类似TCP协议中的三次握手。上图中的B流程。
类似double check机制的确认机制
还是上图中异步回调的过程,A在同步调用B,B返回成功了。这次调用结束了,但是A为了确保,在过一段时间,这个时间可以是几秒,也可以是每天定时处理,再调用B一次,查询一下之前的那次调用是否成功。例如A调用B更新订单状态,这时候成功了,延迟几秒后,A查询B,确认一下状态是否是自己刚刚期望的。上图中的D流程。
总结
上面的几点总结,更多的在业务系统中体现,在超复杂的系统中,数据的一致性,不是说简单的引入啥中间件能够解决的,更多的是根据业务场景,来灵活应对。