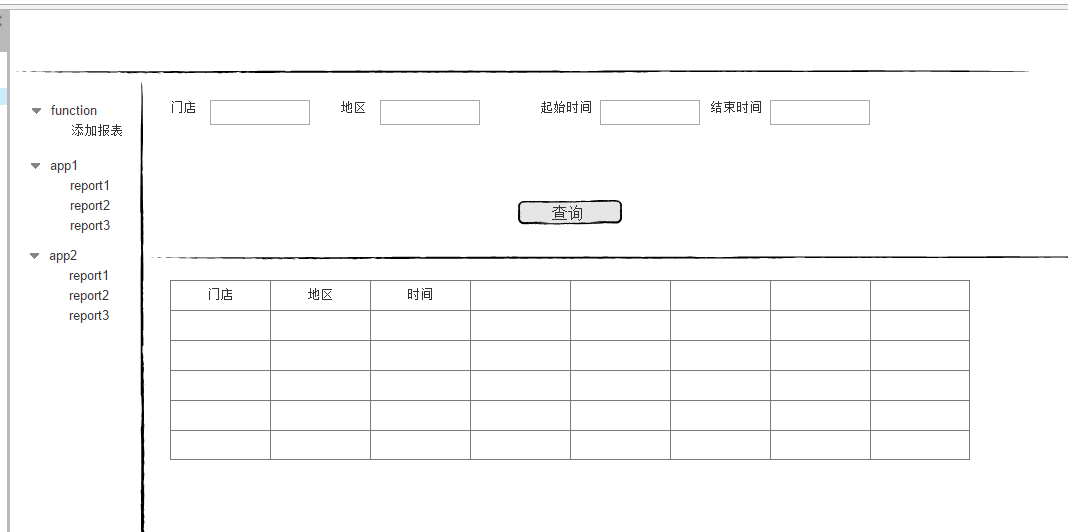
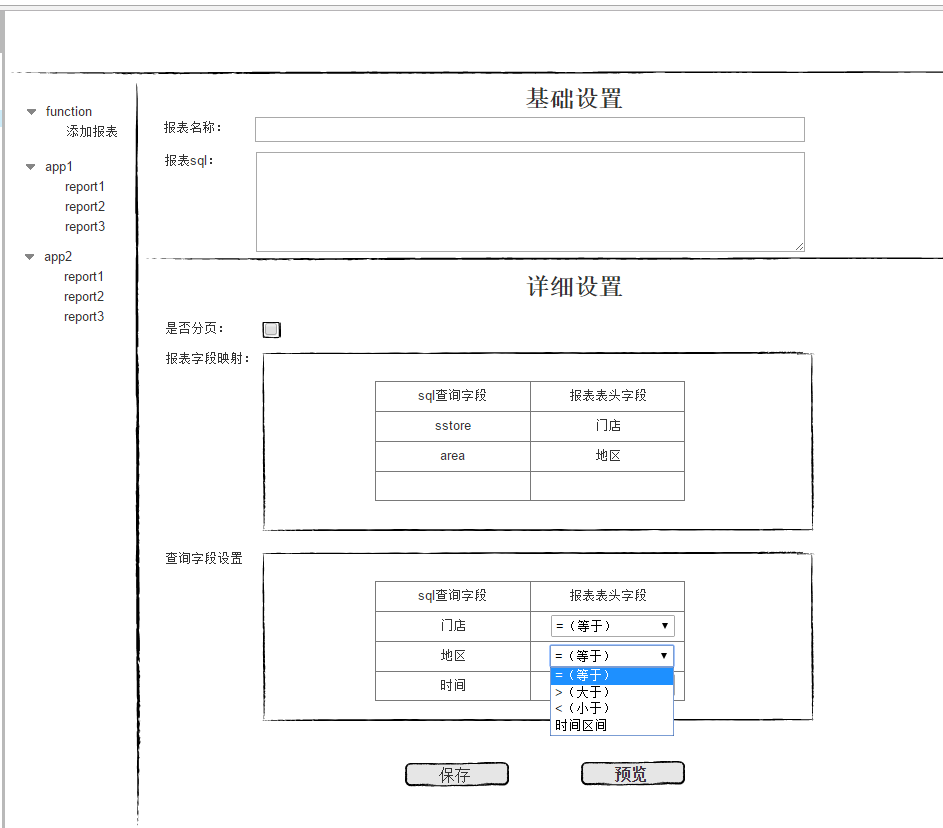
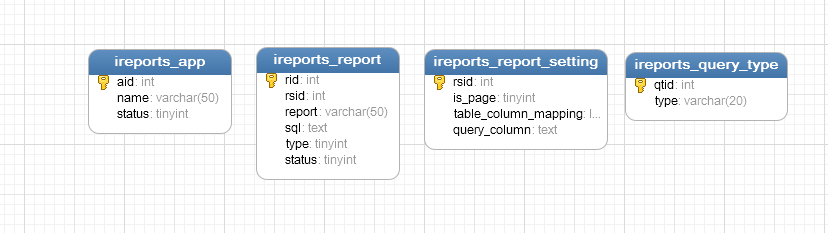
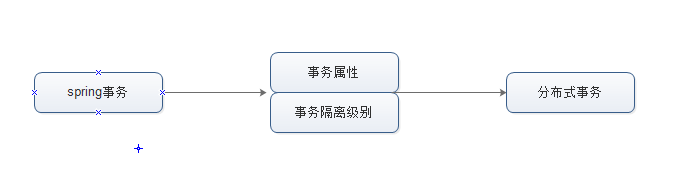
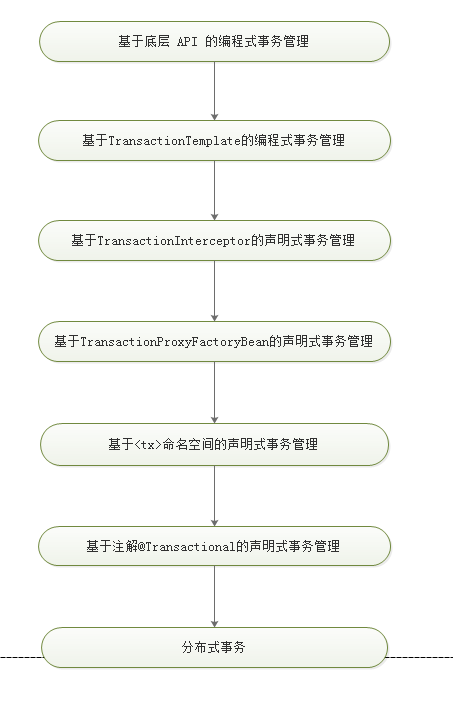
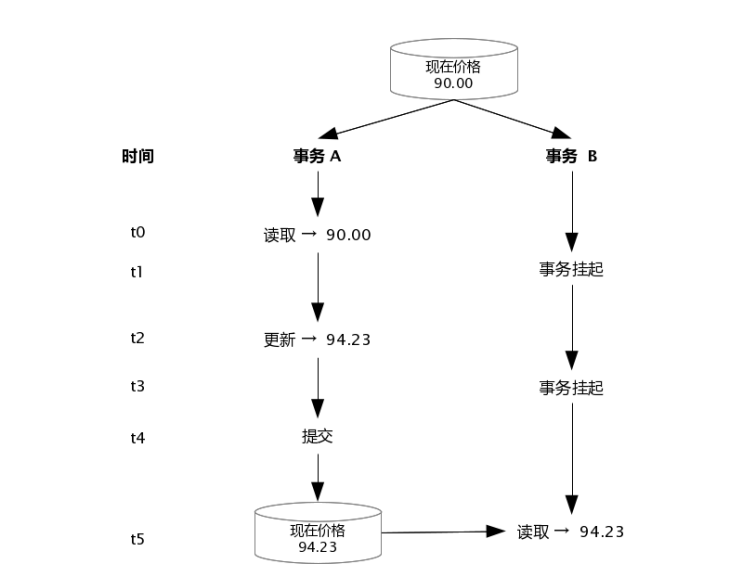
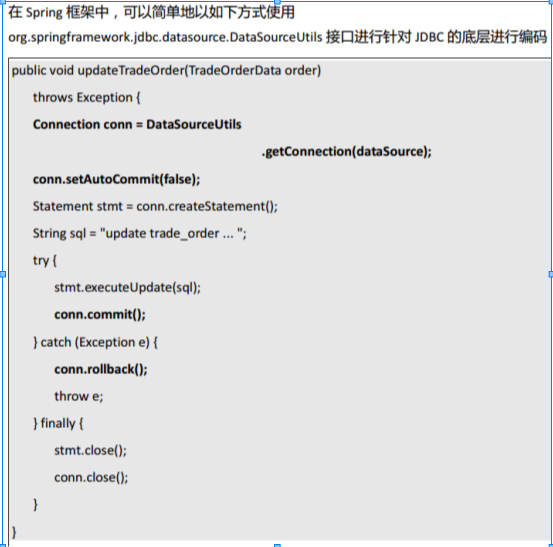
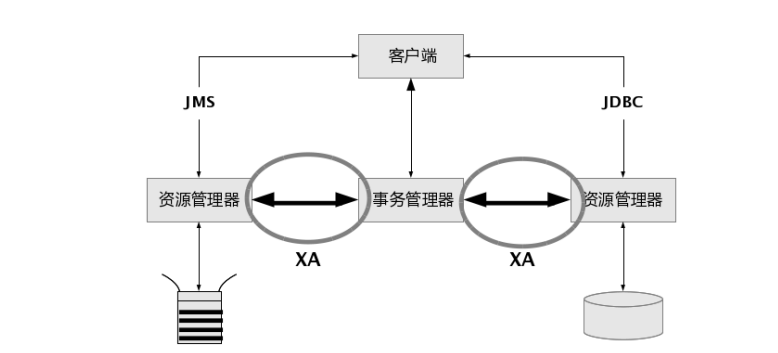
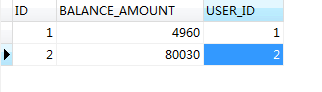
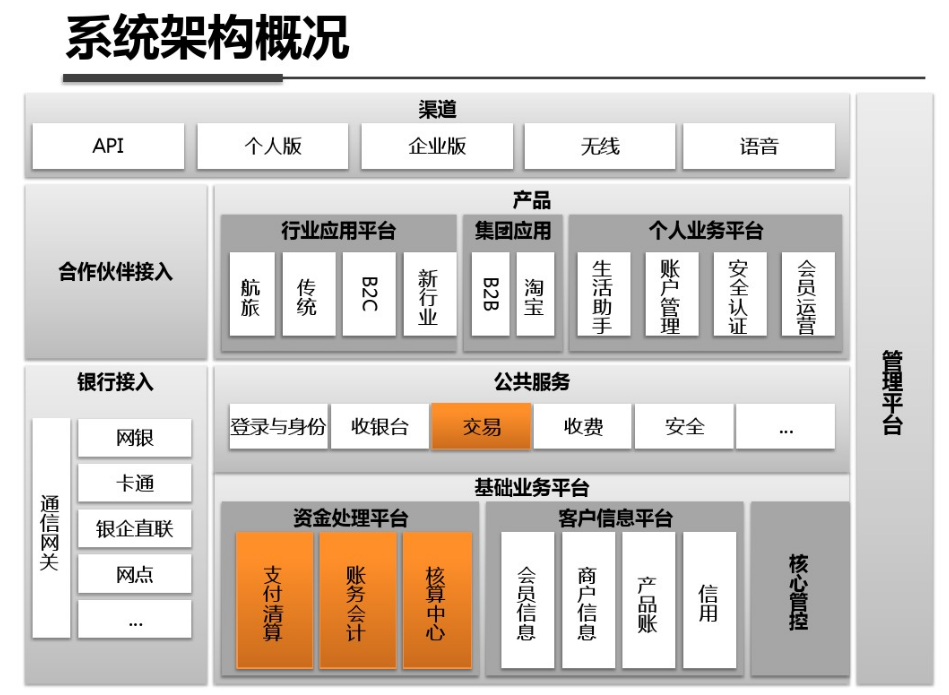
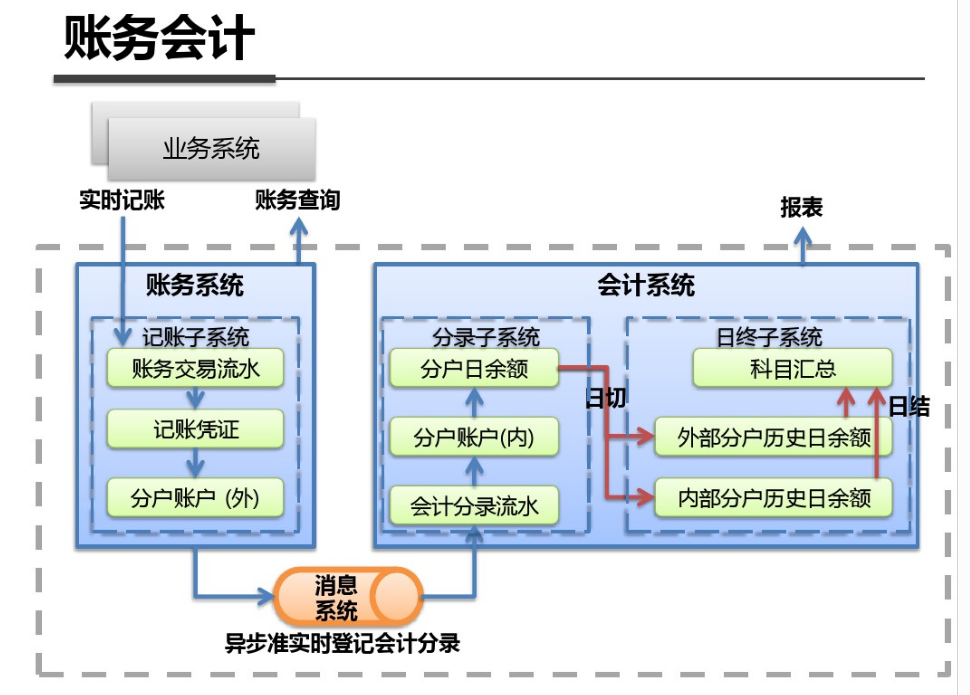
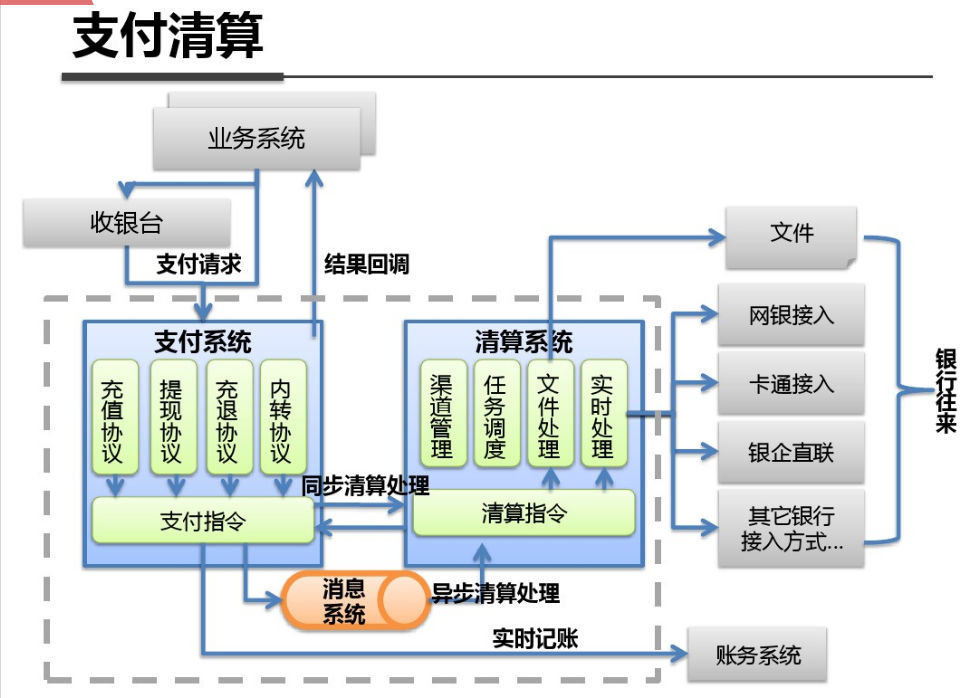
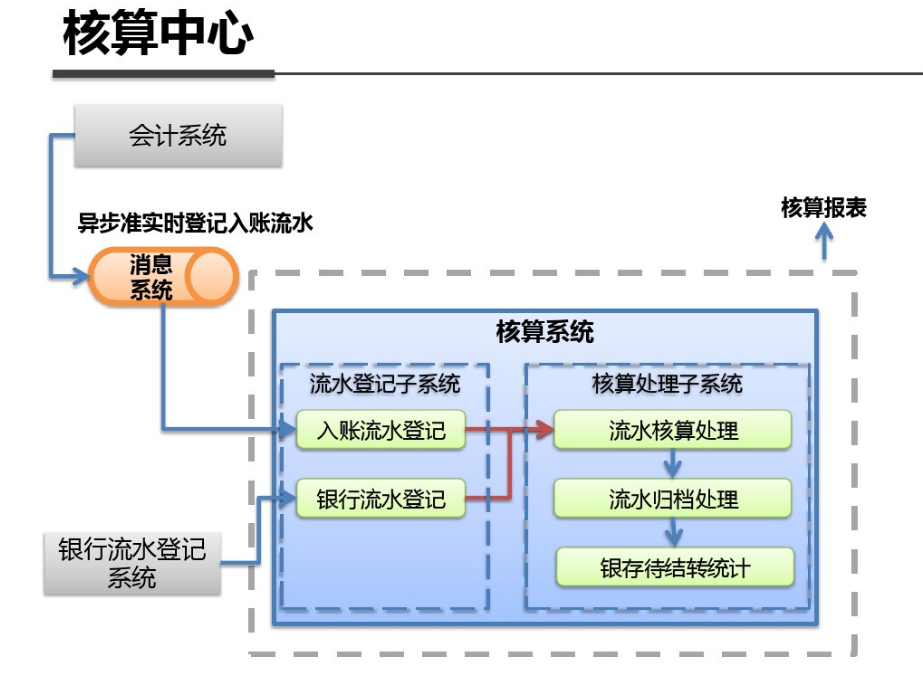
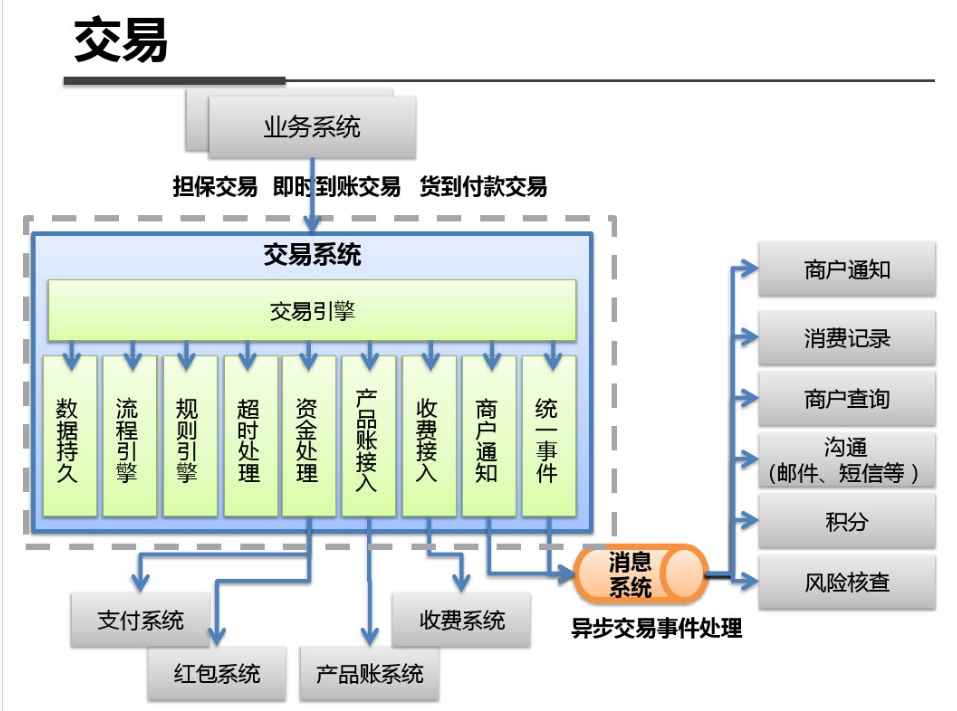
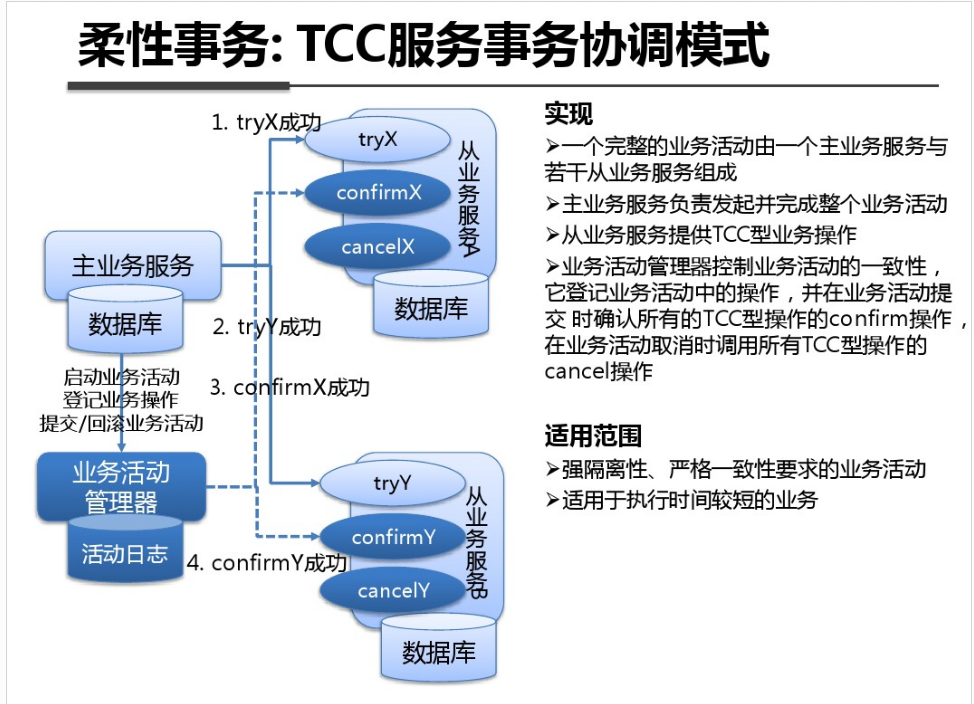
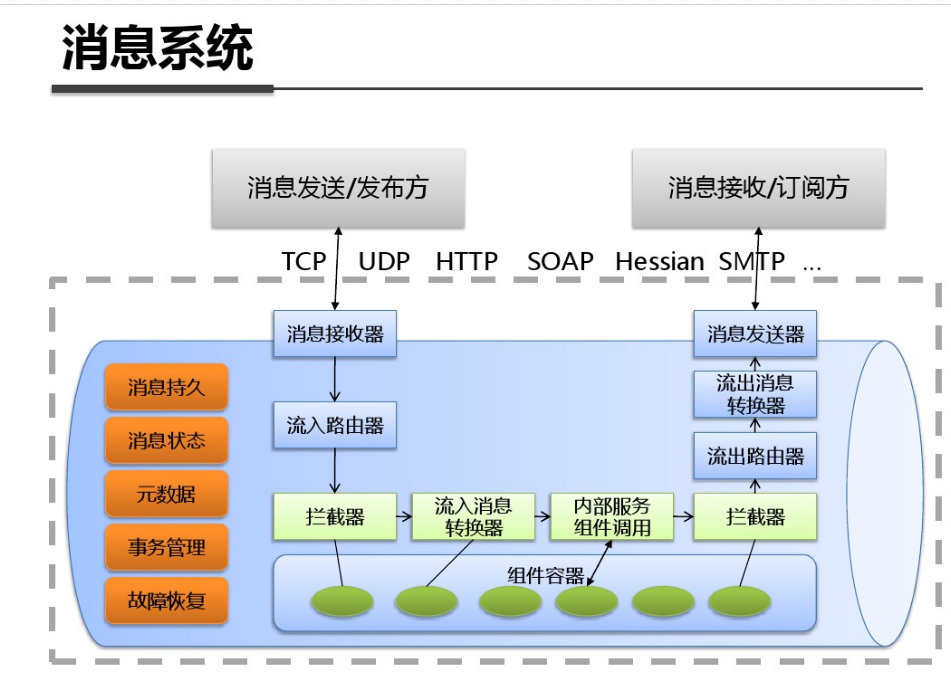
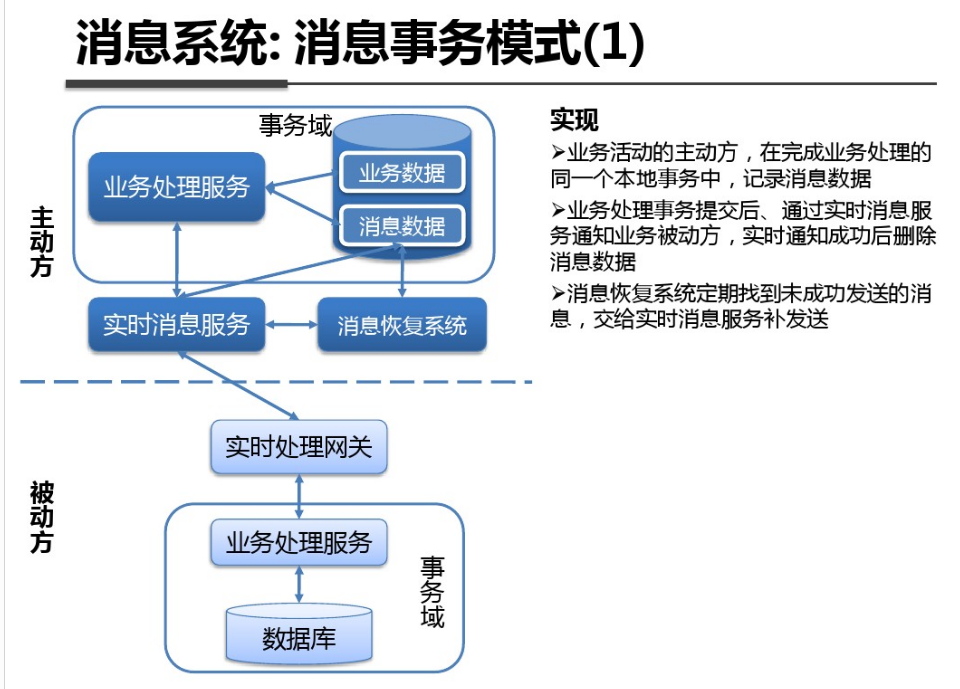
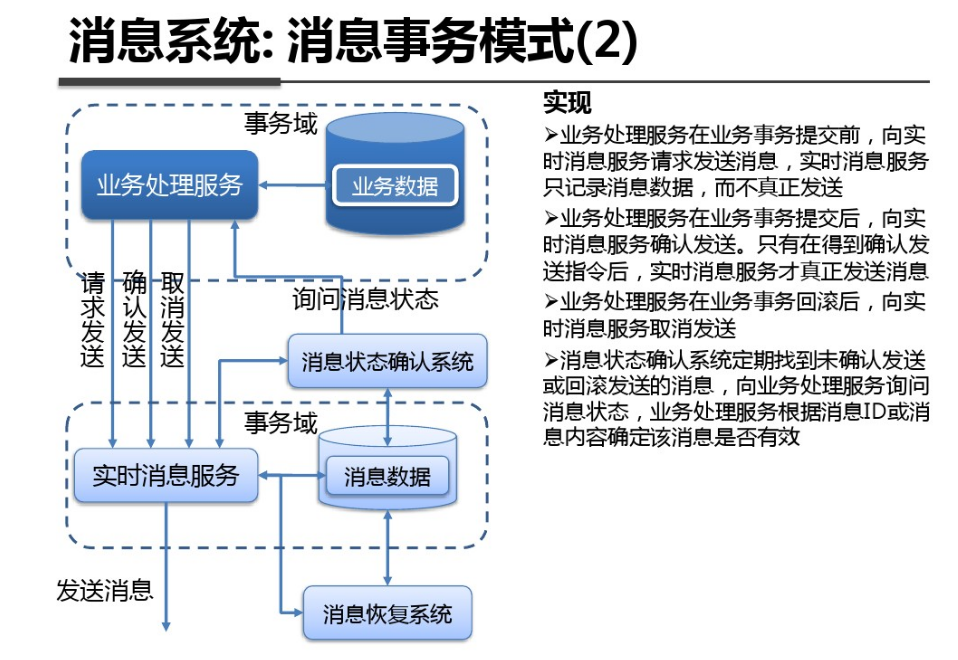
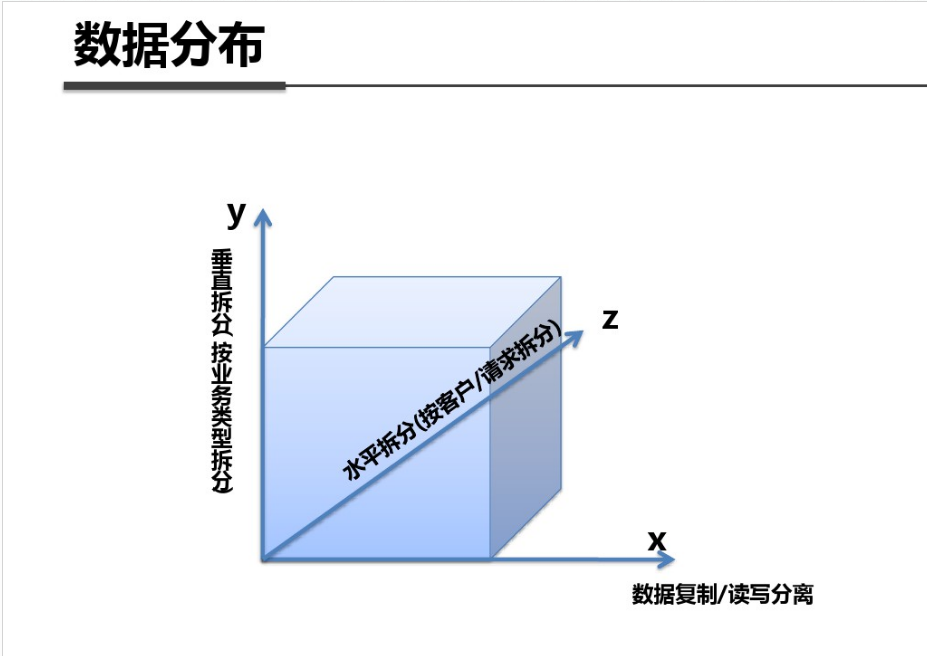
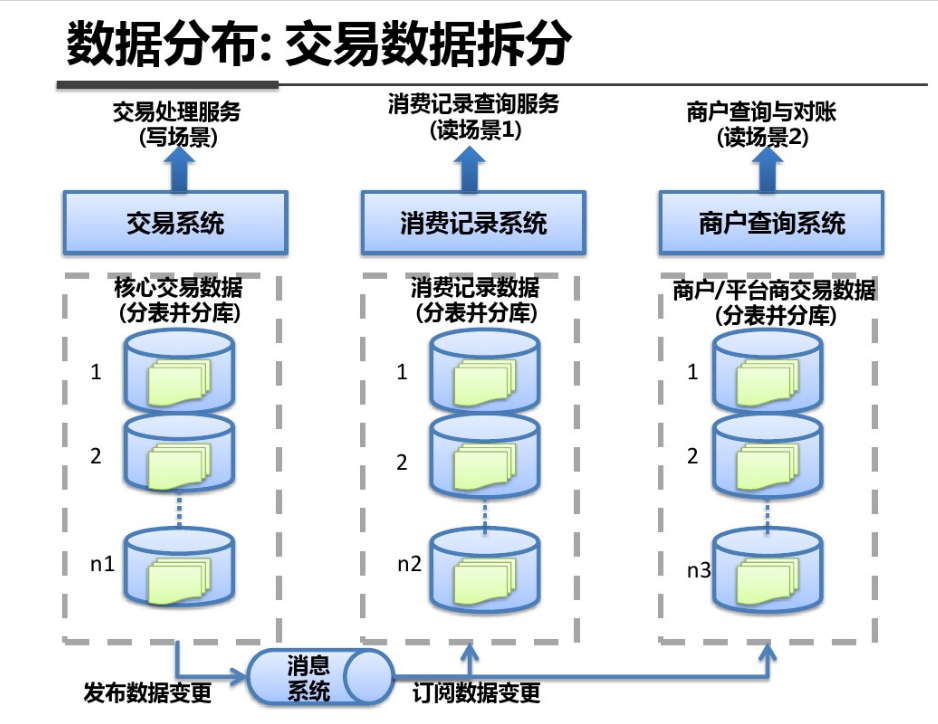
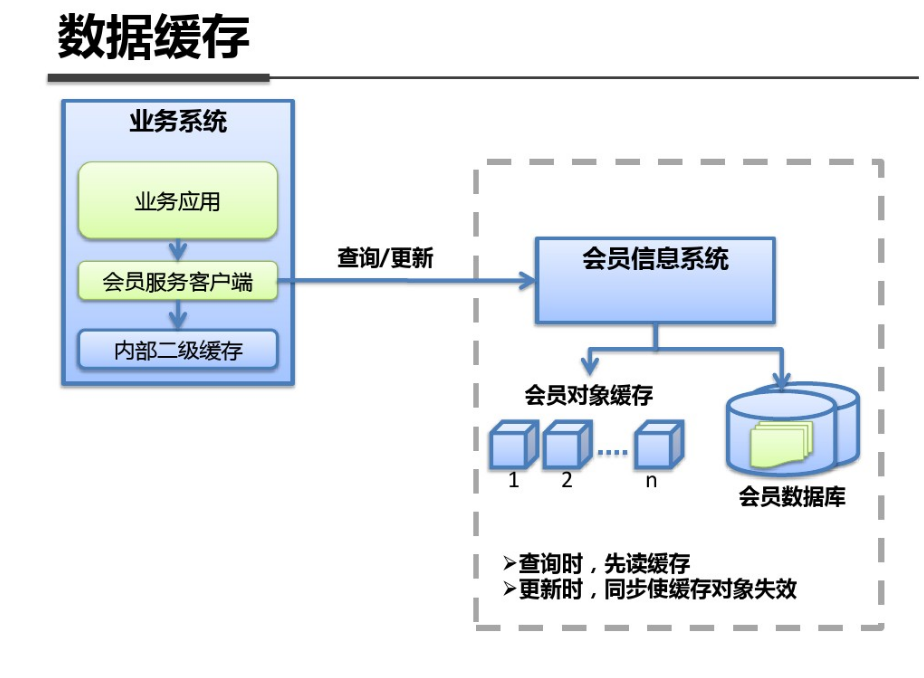
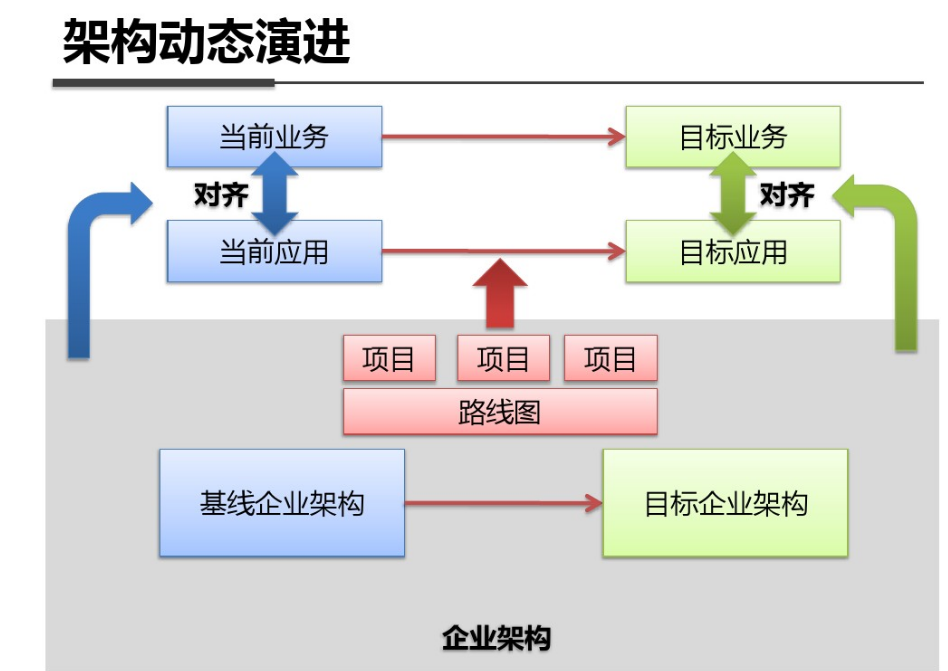
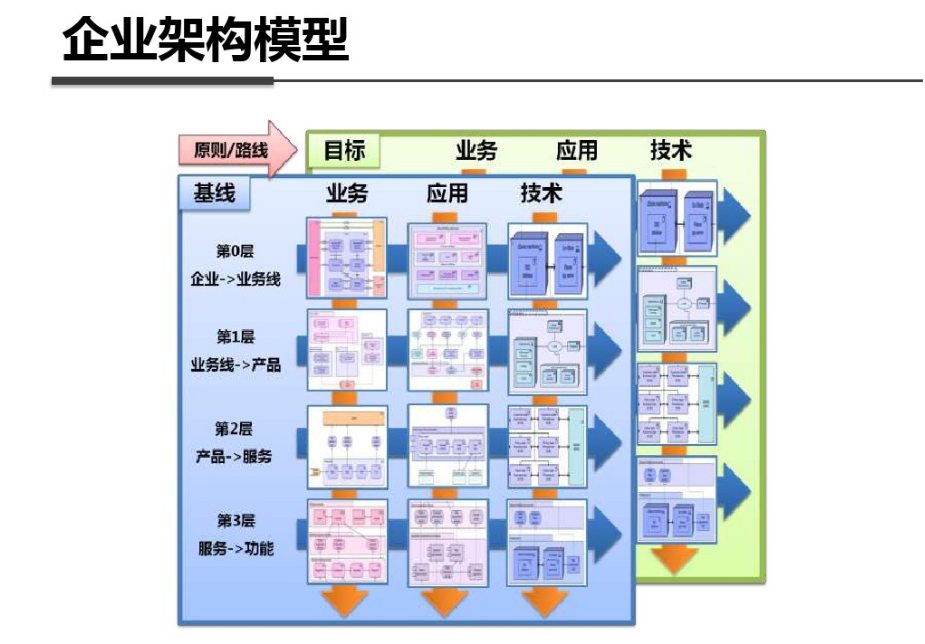
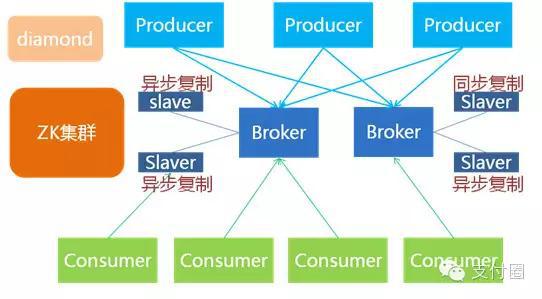
shell是个好东西,服务器上面的操作做多了,就需要想想办法把手工做的事情让脚本帮我们处理。以下是一个针对spring boot项目从svn更新出最新代码,然后maven打包,最后启动发布的一个脚本例子:
1 | #!/bin/bash |
脚本中的“curl -X POST ${url_app}/shutdown”这里是因为使用了spring boot的优雅关闭应用,需要在应用添加maven依赖1
2
3
4<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
然后在配置文件中添加:1
2endpoints.shutdown.enabled=true
endpoints.shutdown.sensitive=false